Traditional Healing Methods
Introduction
Traditional healing has been the cornerstone of human health and well-being for millennia. Long before the advent of modern medicine, various forms of traditional healing—from herbal remedies to spiritual rituals—served as the primary means for treating illnesses and maintaining good health. Rooted in age-old wisdom, these practices often draw from the natural environment and cultural heritage. They encompass a broad range of methodologies, each designed to harmonize the body, mind, and spirit, frequently using resources that are readily available within the community or natural world.
The importance of traditional healing practices is immeasurable, especially in the context of holistic health. While modern medicine focuses on specific symptoms and diseases, often through targeted drugs and surgeries, traditional healing adopts a more comprehensive approach. It aims to balance the human body’s intrinsic energies and capacities for self-healing, viewing health as an interconnected system rather than isolated issues. This makes traditional healing methods highly complementary to modern medicine. For instance, acupuncture can be used in conjunction with pharmaceutical treatments for pain management, and Ayurvedic diets can support conventional nutrition plans.
In today’s world, where the pace of life is fast and stress levels are high, there’s a growing demand for holistic, all-encompassing healthcare solutions. It’s here that traditional healing techniques are gaining renewed interest, not just as alternative treatments but as vital components of integrated healthcare systems. With rising scientific evidence in support of many of these ancient practices, such as the effectiveness of certain herbal remedies or the benefits of mindfulness and meditation, the role of traditional healing is becoming increasingly acknowledged and respected.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into three main categories of traditional healing practices. The first category, Physical Modalities, explores the tangible techniques used for bodily healing, such as crystal healing and acupuncture. The second, Ancient Medicinal Practices, looks at time-tested systems like Traditional Chinese Medicine and Ayurvedic Healing. Finally, the third category focuses on Spiritual and Cultural Healing, diving into practices that engage the mind, spirit, and cultural identity as avenues for health and well-being.
By unpacking these categories, we aim to offer a balanced and informative overview of the rich landscape of traditional healing, setting the stage for a deeper understanding of each practice’s unique contributions to human health.
Physical Modalities

Physical Healing
Physical healing, as a subset of traditional healing modalities, focuses primarily on manipulating the body’s physiological structures to alleviate pain, improve function, and restore balance. It is a vital component of healthcare that complements modern medical approaches. These practices are especially significant because they provide options for individuals seeking less invasive or drug-free alternatives for treatment, paving the way for holistic wellness.
Common techniques in the realm of physical healing include massage, cupping, chiropractic adjustments, and various forms of bodywork. Massage therapy, for instance, involves kneading and manipulating muscles to relieve tension and improve blood flow. Cupping, a practice with origins in both Chinese and Middle Eastern traditional medicine, utilizes suction cups to stimulate circulation and help with pain, inflammation, and relaxation.
These methods have universal elements but are often specialized according to cultural traditions. For example, Shiatsu is a Japanese form of massage that utilizes finger pressure along energy meridians, aiming to balance the body’s chi or vital energy. Swedish massage, originating from Europe, employs long, flowing strokes and is generally geared toward relaxation and increased circulation. Similarly, Thai massage integrates yoga-like stretches to improve flexibility and relieve tension, whereas Native American bone-setting techniques focus on realigning the skeletal system in a manner similar to modern chiropractic care.
Such techniques have not only endured through generations but are also increasingly backed by scientific evidence. Numerous studies have demonstrated the efficacy of massage in reducing stress hormones, improving mood, and even boosting immune function. Cupping has been found useful in certain cases for pain management and improving respiratory conditions.
Importantly, these practices offer a personalized approach to healing. Practitioners typically tailor their techniques to suit individual needs, considering factors like body type, age, and specific health issues. This customization allows for a more nuanced treatment plan that may offer better outcomes than one-size-fits-all medical interventions.
By understanding the various physical modalities used in traditional healing, we can better appreciate the breadth and depth of options available for health and wellness. These practices continue to serve as invaluable resources for those seeking a more integrative and holistic approach to healthcare.

Crystal Healing
Crystal healing is a form of alternative therapy that involves the use of gemstones and crystals to balance and align the body’s energy centers, or chakras. This practice has ancient roots, tracing back to civilizations like the Egyptians, who utilized stones like turquoise and lapis lazuli for protection and health. Similarly, the practice can be found in traditional Vedic texts and Chinese medicine manuscripts, indicating its wide cultural reach.
The fundamental idea is that different types of crystals emit various frequencies or vibrations, which can interact with the human energy field to bring about healing or balance. Some popular crystals and their purported benefits include:
- Rose Quartz: Known as the ‘love stone,’ it is believed to promote emotional healing and open the heart chakra.
- Amethyst: Often used for its calming effects and to enhance intuition.
- Clear Quartz: Said to be a master healer and energy amplifier.
- Black Tourmaline: Commonly used for grounding and protection from negative energy.
- Citrine: Believed to promote abundance and vitality.
The practice of crystal healing is usually highly personalized and can be done in various ways. Some common methods include:
- Direct Placement: Crystals are placed on specific chakras or areas of the body in need of healing.
- Crystal Grids: Multiple stones are arranged in geometric patterns to magnify their collective energy.
- Crystal Elixirs: Water is charged by placing a crystal in it for a period, and the water is then consumed.
- Meditation: Holding a crystal while meditating to incorporate its frequency into the meditative practice.
While the scientific community generally considers crystal healing to be a pseudoscience due to a lack of empirical evidence, many practitioners and users claim to experience tangible benefits. Moreover, the psychological comfort and the ritualistic aspects of the practice can have a placebo effect, which shouldn’t be discounted when considering its therapeutic potential.
Crystal healing serves as another layer within the multifaceted realm of physical modalities in traditional healing. Its history, the variety of crystals used, and the different methods of application all contribute to its enduring popularity for those seeking alternative or complementary therapeutic options. Whether used alone or in conjunction with other treatments, crystal healing offers a unique and personalized approach to physical and emotional well-being.
Acupuncture
Definition and Origin (Traditional Chinese Medicine)
Acupuncture is a key component of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM). It involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to manipulate the flow of Qi (pronounced “Chi”) and bring about healing. This practice is rooted deeply in Chinese philosophy and has been widely used for thousands of years.
Common Uses
Acupuncture is commonly used for various conditions, most notably for pain management. It is also used to treat mental health issues, stress, and chronic conditions like migraines and insomnia.
Scientific Backing
Many scientific studies have investigated acupuncture, and there is evidence supporting its efficacy in treating conditions like chronic pain and migraines. However, the exact mechanisms are not fully understood, and some studies present conflicting results.
Ancient Medicinal Practices
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM)
Traditional Chinese Medicine is a holistic healthcare system that has been practiced for over 2,500 years. The system revolves around the concepts of Yin and Yang, Qi, and the Five Elements—Wood, Fire, Earth, Metal, and Water.
Key Practices in TCM include:
- Herbal Medicine: Utilizes plant extracts and herbs to balance the body’s internal conditions.
- Acupuncture: As mentioned above, it involves inserting needles into the body to manipulate the flow of Qi.
- Tai Chi: A form of exercise that combines movement, meditation, and breath control to improve health.
- Qi Gong: Another mind-body practice aimed at enhancing the Qi through meditation, physical movement, and breathing exercises.
Modern Relevance and Studies
Traditional Chinese Medicine has seen a resurgence in modern times, thanks partly to scientific research validating its effectiveness. Many modern medical institutions now offer TCM therapies alongside conventional treatments, recognizing their potential benefits and the public’s increasing demand for alternative or complementary options.
In summary, Traditional Chinese Medicine is a rich and complex system of health and healing that offers a variety of treatments and philosophies that go beyond the scope of Western medicine. Its practices, such as herbal medicine, acupuncture, and Tai Chi, have proven beneficial for numerous individuals, and its principles continue to intrigue and inspire scientific studies. It’s an invaluable part of the tapestry of ancient medicinal practices that have stood the test of time.
Ayurvedic Healing
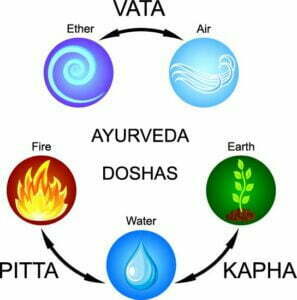
Originating from India over 3,000 years ago, Ayurvedic Healing is one of the world’s oldest healthcare systems. It’s a holistic practice that emphasizes the balance of body, mind, and spirit. The fundamental principles lie in the concept of “Doshas,” which are the three primary energies—Vata, Pitta, and Kapha—that govern physiological and psychological processes in the body.
Key Practices in Ayurveda include:
- Diet: Ayurveda prescribes specific dietary guidelines based on one’s dosha composition. Foods are categorized by their qualities (gunas), tastes, and actions on the body.
- Yoga: Often integrated into Ayurvedic treatment plans, Yoga incorporates physical postures, breathing techniques, and meditation to balance the doshas and promote mental and physical well-being.
- Herbal Treatments: Similar to TCM, Ayurveda also utilizes a variety of herbs and natural substances to treat illnesses. Examples include turmeric, ashwagandha, and neem.
Modern Relevance and Scientific Studies:
Ayurveda has garnered international attention and has become particularly popular in Western countries as a complementary health approach. The body-mind balance that Ayurveda advocates appeals to those seeking holistic care and preventive measures. Scientific studies into Ayurveda are still in nascent stages but are gradually accumulating. For instance, turmeric’s active component, curcumin, has been extensively studied for its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Likewise, ashwagandha has shown promise in reducing stress and anxiety in clinical trials.
The rise of integrative medicine has provided a platform for the resurgence of Ayurvedic practices. Modern healthcare institutions are increasingly incorporating Ayurvedic treatments, such as diet modification and herbal supplements, into their holistic care models.
In summary, Ayurvedic Healing is a comprehensive healthcare system deeply rooted in ancient Indian philosophy and practices. Its focus on individualized treatment, primarily through diet, yoga, and herbal treatments, offers a personalized avenue for health and well-being. While scientific validation is ongoing, Ayurveda continues to gain acceptance in the global healthcare landscape.
Herbal Medicine
Herbal Medicine is a universal form of healing that transcends cultural and geographical boundaries. It holds a pivotal role in various traditional practices around the world, from Traditional Chinese Medicine in Asia to Native American remedies in North America and Ayurvedic treatments in India. Its global importance lies in its accessibility, affordability, and a long-standing history of usage for treating a myriad of conditions.
Common Herbs and Their Uses:
- Ginseng: Used predominantly in East Asia and North America, it is renowned for its energizing properties and is often used to improve focus and combat fatigue.
- Turmeric: Primarily used in South Asia, it is famous for its anti-inflammatory benefits and is a common ingredient in treatments for arthritis and other inflammatory conditions.
- St. John’s Wort: Originating from Europe, it is widely used for mood disorders, particularly depression and anxiety.
- Echinacea: Native to North America, this herb is commonly used to boost the immune system and combat the common cold and other infections.
- Aloe Vera: Used globally but especially prevalent in Africa and India, it’s known for its skin-healing properties, particularly for burns and wounds.
Modern Applications and Scientific Support:
Herbal medicine has seen a renaissance in recent years, partly due to the increase in scientific research validating its effectiveness. Ginseng, for instance, has been shown to improve mental performance in several studies. Turmeric and its active compound, curcumin, have been the subjects of numerous scientific papers attesting to their anti-inflammatory and antioxidant benefits. In a similar vein, St. John’s Wort has undergone various clinical trials, some of which suggest it may be as effective as standard antidepressant medications for mild to moderate depression.
The rise of pharmaceuticals didn’t eclipse the relevance of herbal medicine; instead, it paved the way for integrative medicine. Nowadays, herbal remedies are not just limited to traditional practices but have found their way into mainstream healthcare. Many modern medications are derived from plants, and herbal supplements are commonly used in conjunction with standard medical treatments.
In conclusion, Herbal Medicine is a key player in the realm of ancient medicinal practices. Its global importance is underscored by its widespread use across various traditional healing systems, each with its unique set of herbs and applications. The surge in scientific studies supporting the efficacy of herbal treatments has reinforced its relevance in modern healthcare, making it a versatile, accessible, and effective form of treatment.

Spiritual Healing
Spiritual healing operates on the principle of manipulating energy fields, restoring balance, and invoking inner peace to facilitate physical and emotional well-being. Unlike other forms of traditional healing that directly interact with the physical body, spiritual healing focuses on the immaterial aspects, such as the soul, spirit, or aura.
Common forms of spiritual healing include:
- Reiki: Originating from Japan, Reiki involves a practitioner channeling universal life energy through their hands to promote healing in themselves or others.
- Pranic Healing: Rooted in ancient Indian culture, this form employs the manipulation of the body’s life force or “prana” to restore energy balance.
- Faith Healing: This form is commonly found in religious contexts where prayer or rituals are used to invoke divine intervention for healing.
The Role of Belief and Faith:
One of the foundational elements of spiritual healing is the role of belief and faith, not just in a higher power but also in the efficacy of the healing process itself. The mental and emotional commitment to healing amplifies the effectiveness of these practices, making them deeply personal experiences. In many cases, spiritual healing also entails a journey of self-discovery and empowerment, often leading to transformative life changes.
Scientific Viewpoints:
From a scientific standpoint, spiritual healing is often met with skepticism due to its intangible nature and the absence of empirical evidence. However, aspects like the placebo effect cannot be ignored. The power of belief and the mind-body connection have been well-documented, showing significant results in improving physical and mental conditions. Moreover, psychological studies have indicated that spiritual practices can lead to lower stress levels, improved mental health, and an overall sense of well-being.
Though mainstream science has yet to fully endorse the efficacy of spiritual healing techniques like Reiki and Pranic Healing, these practices have found a place in various healthcare settings, such as hospice care and stress management programs. Their rise in popularity signifies a collective acknowledgement of the limitations of conventional medicine in treating the “whole” human being, thereby opening doors to alternative methods.
In conclusion, Spiritual Healing offers an alternative yet complementary route to health and well-being, addressing the often overlooked aspects of the human experience. While it remains a subject of debate and research within the scientific community, its centuries-old roots and widespread practice across cultures and religions speak to its enduring appeal and potential efficacy. With a focus on the intangible essence of our being, spiritual healing provides a deeply personalized approach to wellness, thereby enriching the multifaceted tapestry of traditional healing methods.
Cultural Healing
Cultural Healing is deeply rooted in the traditions and belief systems of indigenous and local communities around the world. It is often passed down through generations and is integral to the identity and social fabric of these communities. These practices serve not only as a form of healthcare but also as a way to connect with ancestral wisdom, the environment, and the spiritual world.
Importance in Indigenous and Local Communities:
Cultural healing practices hold special significance in indigenous communities, functioning as both curative and preventive care. These practices are often closely linked with the land, using locally sourced herbs, animal products, and sacred sites. They also serve as a form of social cohesion, reinforcing community bonds and preserving a sense of identity and heritage.
Examples:
- Native American Healing Rituals: Practices such as the Sweat Lodge, smudging, and various dance rituals serve as both spiritual and physical healing modalities. They often involve communal participation and the guidance of a Shaman or Medicine Man.
- African Traditional Healing: African healing traditions vary widely across the continent but commonly employ herbal medicines, ancestral worship, and spiritual rituals. Practices such as divination and the use of talismans are also prevalent.
Ethical Considerations:
As interest in traditional healing methods grows globally, so does the risk of cultural appropriation. It’s essential to approach these practices with sensitivity and respect, acknowledging their sacred nature and the communities from which they originate.
Another critical issue is the unsustainable or unethical use of herbs and animal parts, which can lead to environmental degradation and endangerment of species. For example, the use of rhino horn in some traditional medicines has contributed to the endangerment of the rhinoceros.
In conclusion, Cultural Healing offers a rich tapestry of practices and beliefs that have sustained indigenous and local communities for generations. While the world is becoming increasingly interested in these ancient wisdoms, it’s crucial to engage with them ethically and respectfully. These practices are not just “alternative therapies” but are vital aspects of cultural identity and heritage. Therefore, ethical considerations must be at the forefront when engaging with cultural healing, to honor and preserve their roots and to sustain the environments and communities that hold this knowledge.
Conclusion
As we navigate the complexities of modern healthcare, the role of traditional healing methods remains not only relevant but increasingly vital. These ancient practices offer holistic approaches to well-being that address the body, mind, and spirit, often filling the gaps left by conventional medicine. They serve as both preventive and curative options, sometimes offering solutions where modern treatments have limitations or adverse effects.
Summary of the Three Main Categories:
- Physical Modalities: Techniques like massage, cupping, and acupuncture offer tangible benefits for physical well-being, often backed by emerging scientific evidence. Practices like crystal healing tap into the energy fields to bring about bodily balance.
- Ancient Medicinal Practices: Systems like Traditional Chinese Medicine and Ayurvedic Healing offer comprehensive healthcare solutions that have stood the test of time. Herbal Medicine, deeply ingrained in multiple cultures, has found validation through modern scientific studies.
- Spiritual and Cultural Healing: These practices offer a nuanced view of health, incorporating elements of belief, spirituality, and cultural identity. While not universally backed by scientific evidence, they play an essential role in holistic well-being and are being incorporated more and more into conventional healthcare settings.
Future Directions:
Delving into the world of traditional healing provides a rich tapestry of ancient wisdom that complements modern medicine. As integrative medicine gains traction, it harnesses the best of both realms, promoting a balanced and holistic approach to patient care. Ongoing research is continuously shedding light on the efficacy of these age-old practices, paving the way for their broader acceptance and application.
Moreover, the discourse around the ethics of traditional healing is gaining momentum, highlighting vital concerns related to cultural appropriation and the sustainability of our natural resources.
In essence, traditional healing not only adds layers of depth and diversity to the healthcare paradigm but also serves as a bridge between ancient knowledge and contemporary scientific practices. As we further explore the multifaceted categories of traditional healing, we can better appreciate the vast array of tools at our disposal for enhancing health and well-being. The future beckons a healthcare framework that seamlessly blends the old with the new, rooted in ethics and propelled by continuous research.
Traditional Healing
- Understanding traditional African healing – www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- What Is Traditional Healing? | SoulAdvisor – www.souladvisor.com
- How Have Traditional Healing Practices Been Integrated Into … – iCliniq – www.icliniq.com
- Traditional, Complementary and Integrative Medicine – www.who.int
- Honoring Traditional Healing Practices in Global Health – globalhealth.duke.edu